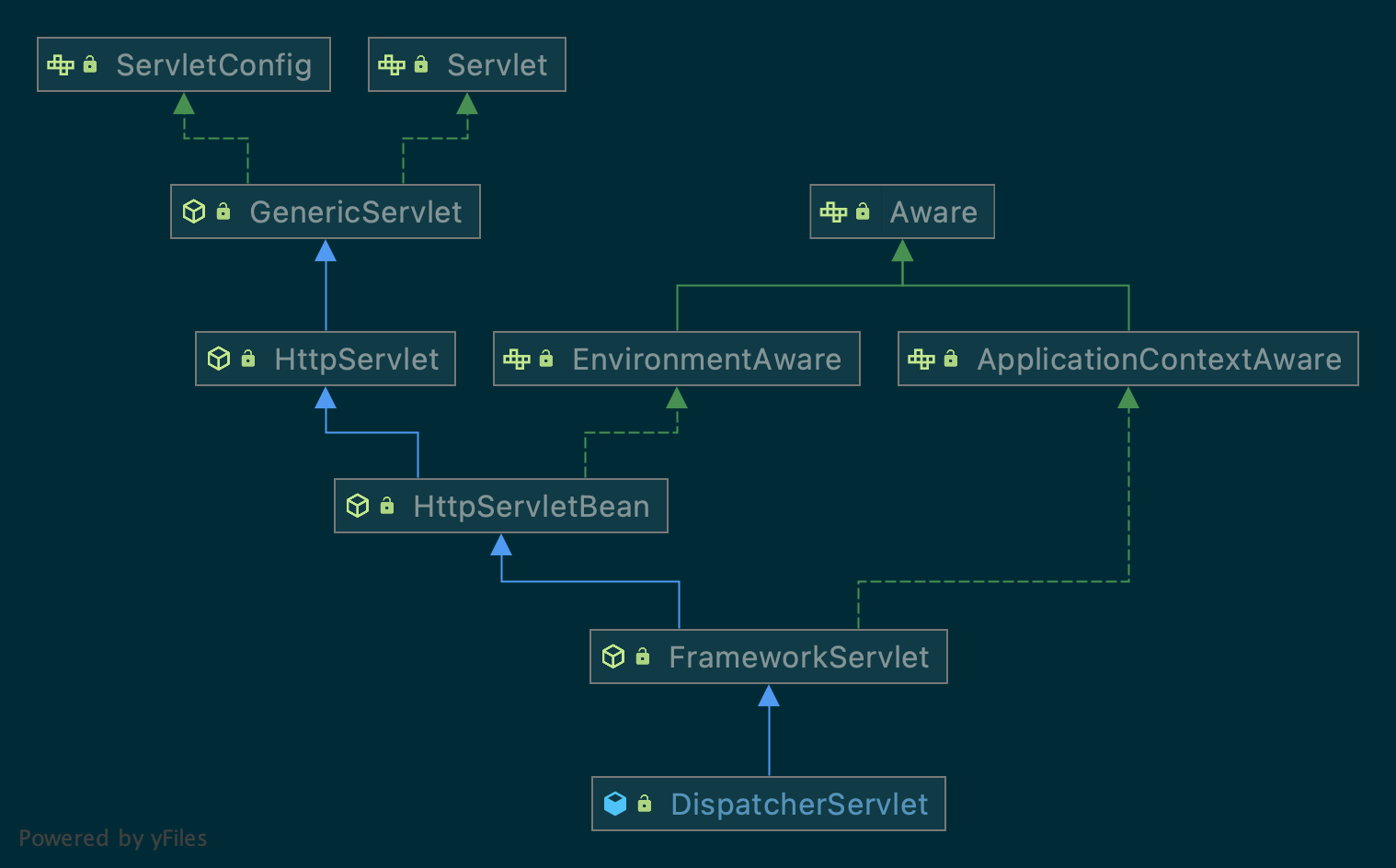
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC中用来分派用户请求的Servlet。

DispatcherServlet是由一系列实现特定功能的策略对象组成的,这些策略对象相互组合,共同了SpringMVC的核心功能。Spring对这些策略对象进行管理,并提供了了一套默认的配置,同样也提供了灵活的扩展与功能改写。
| Bean类名 | Bean名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
MultipartResolver |
multipartResolver |
在相应的解析策略支持下,对multi-part请求(比如浏览器的表单文件上传)进行解析。 |
LocaleResolverLocaleContextResolver |
localeResolver |
解析客户端当前请求的区域信息,从而能够返回该地区的国际化视图。 |
ThemeResolver |
themeResolver |
解析当前应用的主题,从而提供个性化布局 |
HandlerMapping |
handlerMapping |
将请求映射到处理程序以及用于预处理和后续处理的一系列拦截器。 这种映射有着一套标准,具体的功能因 HandlerMapping 实现而异。 HandlerMapping 的两个最主要实现是 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 和 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping ,前者支持 @RequestMapping 注释方法,它为请求的处理进行 URI 映射的注册。 |
HandlerAdapter |
handlerAdapter |
协助 DispatcherServlet 调用匹配请求映射的处理程序,且不需要关心如何调用处理程序以及处理程序的任何细节。 例如,调用带注释的控制器中的方法需要先对 @RequestMapping 等注释进行解析。 HandlerAdapter 的主要功能是屏蔽 DispatcherServlet 的实现细节。 |
HandlerExceptionResolver |
handlerExceptionResolver |
异常处理策略,可以处理HandlerMethod中抛出的异常,但不能处理视图渲染过程中的异常。 |
RequestToViewNameTranslator |
viewNameTranslator |
|
ViewResolver |
viewResolver |
将处理程序返回的逻辑视图名称(String)解析为真实视图并返回给客户。 |
FlashMapManager |
flashMapManager |
存储和检索可将参数从一个请求传递到另一个请求的“输入”和“输出”的 FlashMap,通常通过重定向来实现。 |
DispatcherServlet本质是一个Servlet,因此,其初始化的入口为init()方法:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
/**
* 1、调用 {@link MultipartResolver#isMultipart(HttpServletRequest)}方法检测请求是否是文件上传,
* 如果是,则调用 {@link MultipartResolver#resolveMultipart(HttpServletRequest)} 对请求进行解析
*/
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
/**
* 2、逐个调用 {@link HandlerMapping#getHandler(HttpServletRequest)}方法,以获取 {@link HandlerExecutionChain}对象实例
*/
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
/**
* 3、逐个调用 {@link HandlerAdapter#supports(Object)}}方法,找到第一个支持处理 Handler 的 {@link HandlerAdapter}
*/
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
/**
* 4、处理 GET|HEAD 请求中的 last-modified 请求头
*/
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
/**
* 5、触发拦截器 {@link HandlerInterceptor#preHandle(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object) }方法
*/
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
/**
* 6、调用 {@link HandlerAdapter#handle(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object)}方法真实处理 {@code handler}
*/
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
/**
* 7、从 Request 翻译视图名称 {@link RequestToViewNameTranslator#getViewName(HttpServletRequest)}
*/
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
/**
* 8、触发拦截器的 {@link HandlerInterceptor#postHandle(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object, ModelAndView)} 方法
*/
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
/**
* 9、处理 DispatchResult
*/
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
} catch (Exception ex) {
/**
* 10、触发 {@link HandlerInterceptor#afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object, Exception)}方法
*/
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
} catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
/**
* 11、触发 {@link AsyncHandlerInterceptor#afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object)}方法
*/
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
/**
* 12、如果是文件上传请求,则清理 {@link MultipartResolver#cleanupMultipart(MultipartHttpServletRequest)}
*/
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
checkMultipart()方法中调用MultipartResolver的isMultipart()方法检测当前请求HttpServletRequest是否是文件上传,如果是,则用resolveMultipart()来解析当前请求。getHandler()方法逐个调个HandlerMapping的getHandler()方法,以获取HandlerExecutionChain实例,如果未获取到,则抛出异常NoHandlerFoundException或直接返回404。HandlerAdapter的supports()方法,以找到能够处理当前Handler 的HandlerAdapter实例;Get或HEAD请求中的last-modified请求头;HandlerExecutionChain触发拦截器HandlerInterceptor的preHandle()方法;HandlerAdapter的handle()方法真实处理handler;RequestToViewNameTranslator的getViewName()方法,从请求中获取视图名;HandlerExecutionChain的applyPostHandle()方法触发拦截器HandlerInterceptor的postHandle()方法;HandlerExecutionChain的triggerAfterCompletion()方法触发拦截器的afterCompletion()方法;HandlerExecutionChain的applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted()方法触发拦截器的afterConcurrentHandlingStarted()方法;MultipartResolver的cleanupMultipart()方法清理现场。